ESP-IDF Setup
Overview
This section demonstrates how to set up the ESP-IDF development environment for building and running applications on ESP32 SoCs.
This project uses ESP-IDF v5.3.2, locked to commit fb25eb0.
Step 1: Install Prerequisites
The following packages are required for the ESP-IDF development environment:
idf.py uses #!/usr/bin/env python in its shebang, which expects the python command to be available. On Ubuntu 20.04 and later, python is not included by default, as Python 2 has been deprecated. Check with:
If python is missing, a symlink can be created to point to python3:
Step 2: Get ESP-IDF
Step 3: Set up the Tools
For newer versions of Ubuntu, the install.sh script may not work as expected because `
ESP-IDF provides a script install.sh that installs the required tools such as the compiler, debugger, Python packages, etc.:
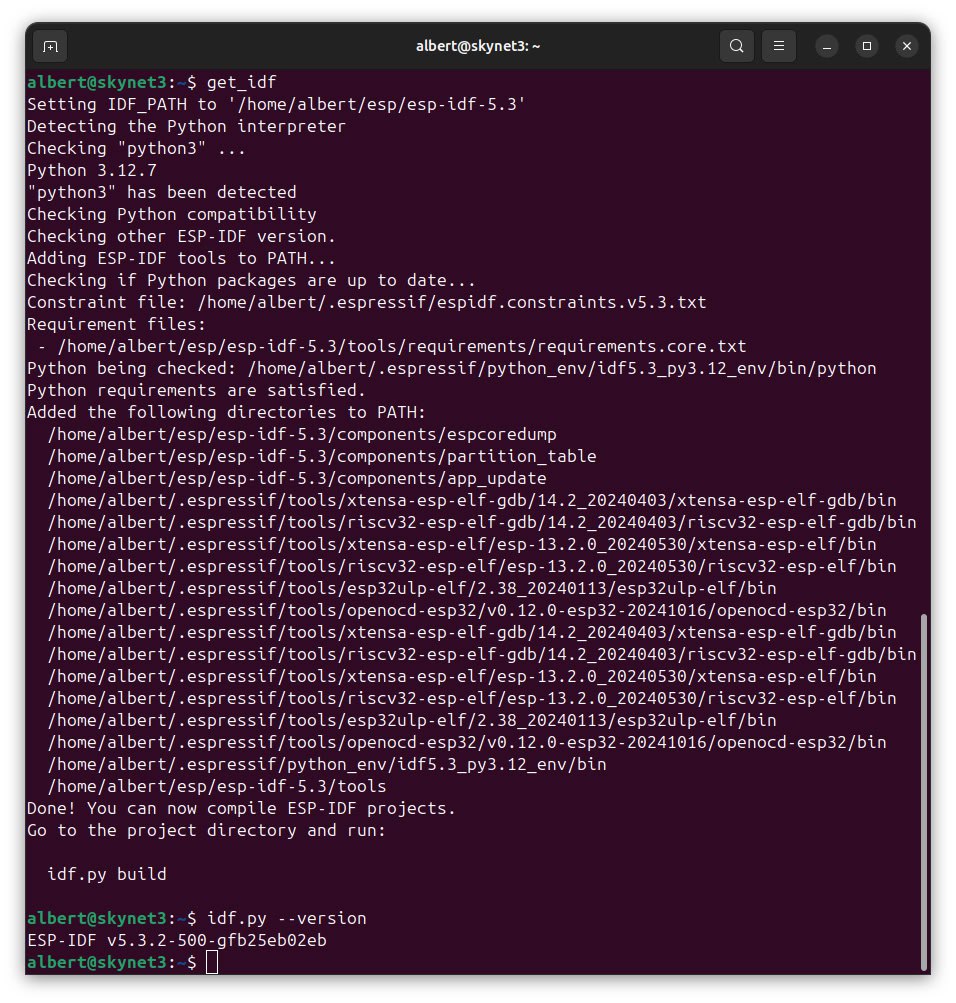
Step 4: Create get_idf Alias
ESP-IDF provides a script export.sh that sets environment variables so the tools are usable from the command line. The script sets IDF_PATH, updates PATH with ESP-IDF tools, verifies Python compatibility, and enables idf.py auto-completion.
Create an alias for executing export.sh by adding the following line to ~/.bashrc file:
Step 5: Refresh Configuration
Restart your terminal session or run:
Now, running get_idf will set up or refresh the esp-idf environment in any terminal session.