CHIP-Tool
Overview
CHIP Tool is a Matter Controllers implementation that allows to commission a Matter device into a network and to communicate with it. It is used for testing and debugging Matter devices.
CHIP Tool was built and installed on a Raspberry Pi 4 Model B (4GB RAM and 32GB SD card) running Ubuntu Server for Raspberry Pi 24.04.1 LTS. Raspberry Pi Imager v1.8.5 was used to flash the Ubuntu image onto the SD card.
Matter v1.4.0.0 SDK was used to build the CHIP-Tool application.
Raspberry Pi Setup
This section outlines the steps to set up a Raspberry Pi as a Matter controller using CHIP-Tool. The process is time-consuming.
Step 1. Ubuntu installation
Install the OS
Download the Ubuntu Server image from the Ubuntu website.
Download and install Raspberry Pi Imager on Ubuntu Desktop:
sudo apt update sudo apt install rpi-imagerInsert the SD card into card reader and connect it to the computer.
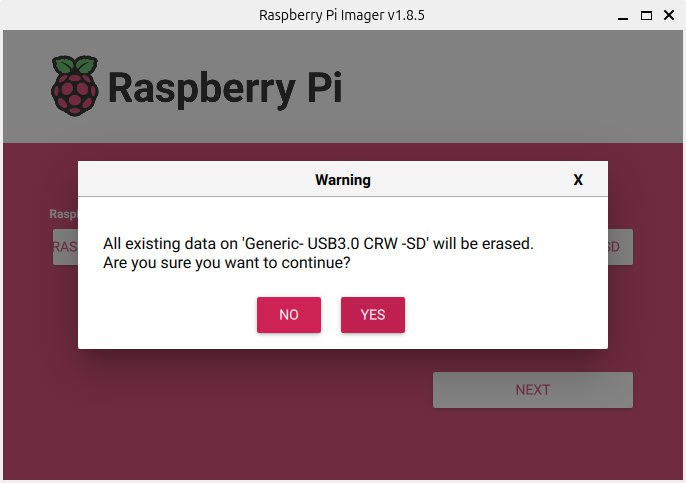
Select the Ubuntu image and the SD card in Raspberry Pi Imager.
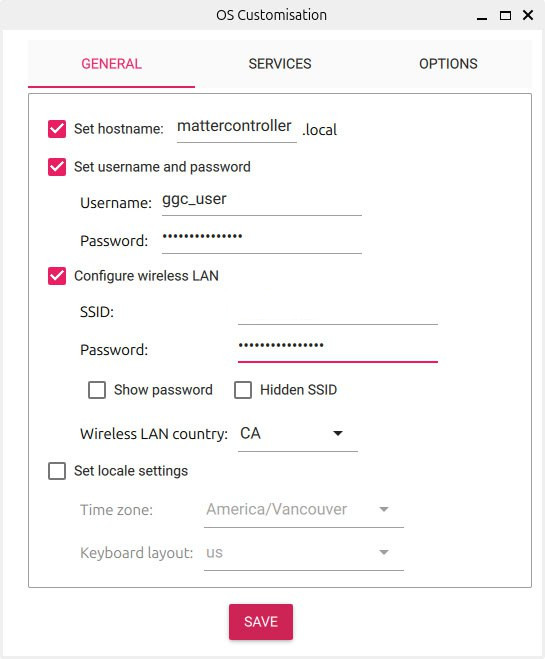
Edit Settings (Wi-Fi and SSH credentials and enable SSH) and flash the image onto the SD card.
Step 2. Connecting to Raspberry Pi
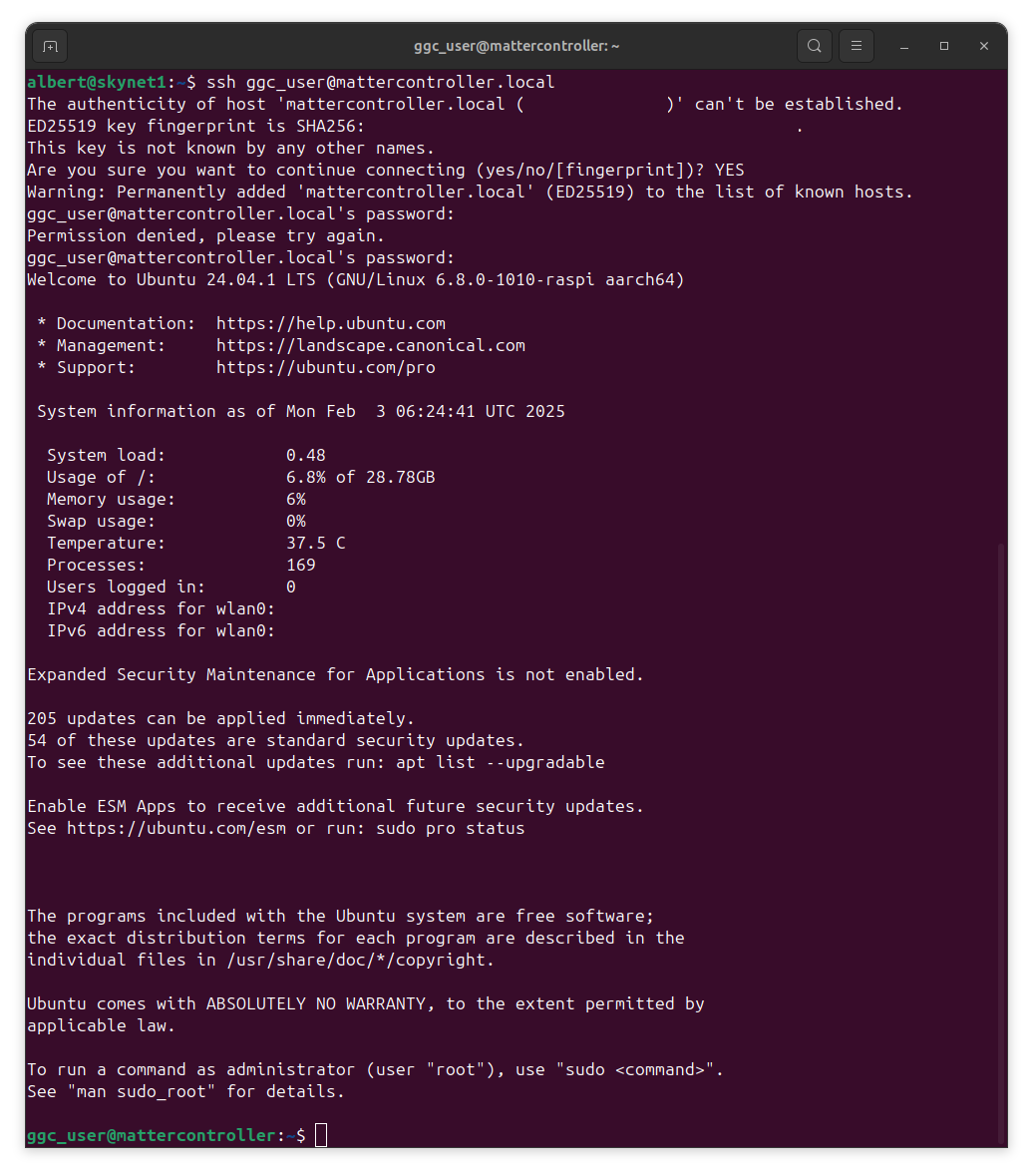
Insert the SD card into the Raspberry Pi and power it on. It will automatically connect to Wi-Fi using the credentials provided during the installation process. It can take a few minutes for the Raspberry Pi to boot up. Once it is ready, connect to it using SSH with the credentials provided during the installation process.
Step 3. Installing Pre-requisites
Update the system and install Raspberry Pi-specific dependencies:
sudo apt update sudo apt upgrade sudo apt-get install git gcc g++ pkg-config libssl-dev libdbus-1-dev \ libglib2.0-dev libavahi-client-dev ninja-build python3-venv python3-dev \ python3-pip unzip libgirepository1.0-dev libcairo2-dev libreadline-dev \ default-jre sudo apt-get install bluez avahi-utils sudo reboot ssh ggc_user@mattercontroller.localEdit the
bluetooth.serviceunit:sudo systemctl edit bluetooth.serviceAdd the following content:
[Service] ExecStart= ExecStart=/usr/sbin/bluetoothd -E -P battery Restart=always RestartSec=3Enable and Start the Bluetooth service:
sudo systemctl start bluetooth.serviceEdit the dbus-fi.w1.wpa_supplicant1.service file:
sudo nano /etc/systemd/system/dbus-fi.w1.wpa_supplicant1.serviceReplace the line #11 with:
ExecStart=/usr/sbin/wpa_supplicant -u -s -O /run/wpa_supplicantEdit the wpa_supplicant.conf file:
sudo nano /etc/wpa_supplicant/wpa_supplicant.confAdd the following content:
ctrl_interface=DIR=/run/wpa_supplicant update_config=1Reboot the Raspberry Pi:
sudo reboot ssh ggc_user@mattercontroller.local
Step 4. Building CHIP Tool
The application will require installation of Matter SDK on Raspberry Pi:
Clone the Matter SDK repository:
mkdir matter cd ~/matter git clone https://github.com/project-chip/connectedhomeip.git cd connectedhomeip/ git checkout tags/v1.4.0.0Prepare Matter SDK:
./scripts/checkout_submodules.py --shallow --platform linux source ~/matter/connectedhomeip/scripts/activate.sh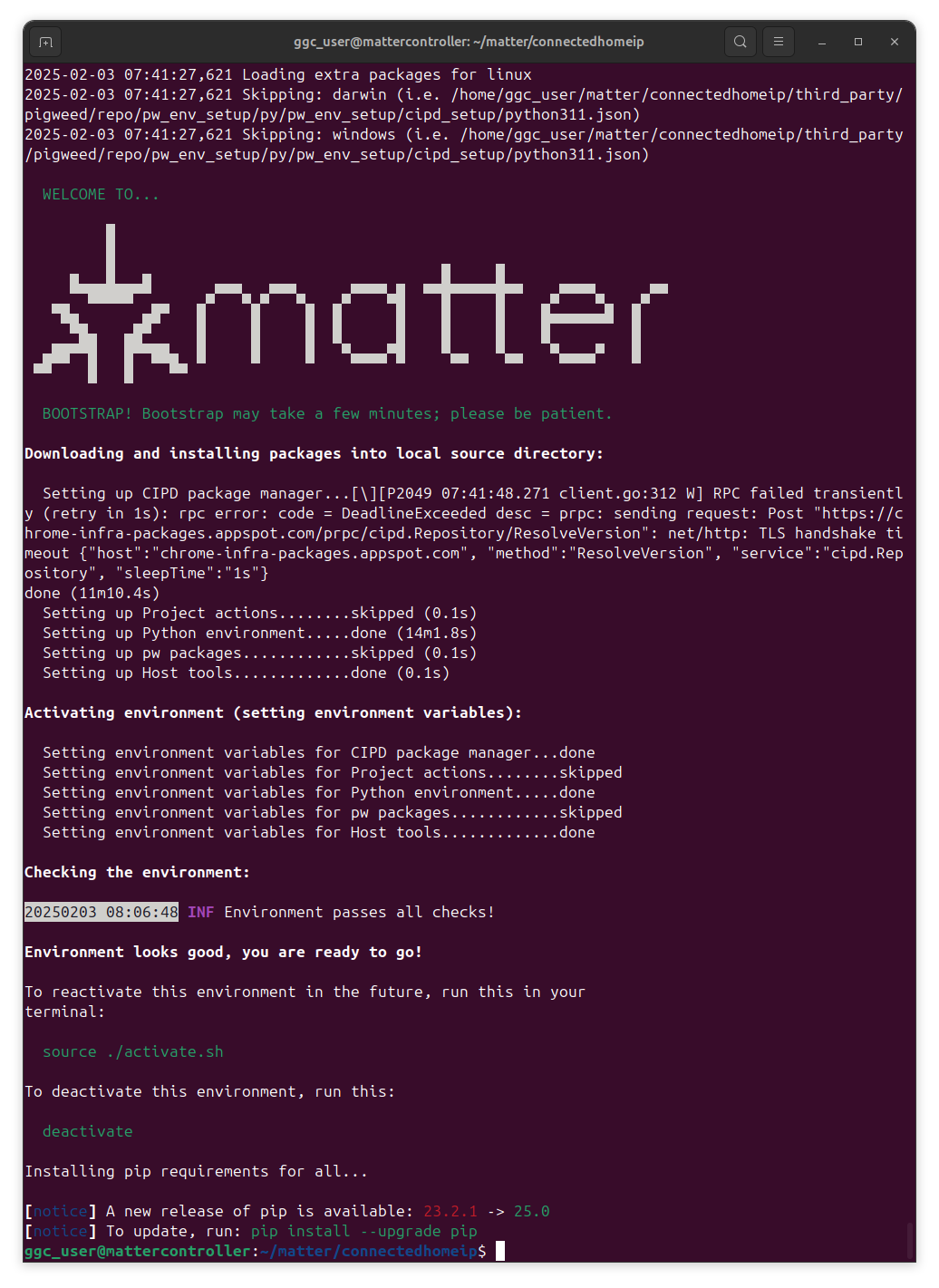
Build CHIP Tool using build_examples.py:
The
targetscommand retrieves supported build targets listed below:./scripts/build/build_examples.py targetsAmeba:
amebad-{all-clusters, all-clusters-minimal, light, light-switch, pigweed}
ASR:
asr-{asr582x, asr595x, asr550x}-{all-clusters, all-clusters-minimal, lighting, light-switch, lock, bridge, temperature-measurement, thermostat, ota-requestor, dishwasher, refrigerator}Optional flags:
[-ota] [-shell] [-no_logging] [-factory] [-rotating_id] [-rio]
Android:
android-{arm, arm64, x86, x64, androidstudio-arm, androidstudio-arm64, androidstudio-x86, androidstudio-x64}-{chip-tool, chip-test, tv-server, tv-casting-app, java-matter-controller, kotlin-matter-controller, virtual-device-app}Optional flags:
[-no-debug]
Bouffalolab:
bouffalolab-{bl602dk, bl704ldk, bl706dk, bl602-night-light, bl706-night-light, bl602-iot-matter-v1, xt-zb6-devkit}-lightOptional flags:
[-ethernet] [-wifi] [-thread] [-easyflash] [-littlefs] [-shell] [-mfd] [-rotating_device_id] [-rpc] [-cdc] [-mot] [-resetcnt] [-memmonitor] [-115200] [-fp]
Texas Instruments (TI):
cc32xx-{lock, air-purifier}ti-cc13x4_26x4-{lighting, lock, pump, pump-controller}Optional flags:
[-mtd] [-ftd]
Cypress (Infineon):
cyw30739-{cyw30739b2_p5_evk_01, cyw30739b2_p5_evk_02, cyw30739b2_p5_evk_03, cyw930739m2evb_01, cyw930739m2evb_02}-{light, light-switch, lock, thermostat}Silicon Labs (EFR32):
efr32-{brd2704b, brd4316a, brd4317a, brd4318a, brd4319a, brd4186a, brd4187a, brd2601b, brd4187c, brd4186c, brd2703a, brd4338a, brd2605a}-{window-covering, switch, unit-test, light, lock, thermostat, pump, air-quality-sensor-app}Optional flags:
[-rpc] [-with-ota-requestor] [-icd] [-low-power] [-shell] [-no-logging] [-openthread-mtd] [-heap-monitoring] [-no-openthread-cli] [-show-qr-code] [-wifi] [-rs9116] [-wf200] [-siwx917] [-ipv4] [-additional-data-advertising] [-use-ot-lib] [-use-ot-coap-lib] [-no-version] [-skip-rps-generation]
Espressif (ESP32):
esp32-{m5stack, c3devkit, devkitc, qemu}-{all-clusters, all-clusters-minimal, energy-management, ota-provider, ota-requestor, shell, light, lock, bridge, temperature-measurement, tests}Optional flags:
[-rpc] [-ipv6only] [-tracing] [-data-model-disabled] [-data-model-enabled]
General:
genio-lighting-app
Linux:
linux-fake-testsOptional flags:
[-mbedtls] [-boringssl] [-asan] [-tsan] [-ubsan] [-libfuzzer] [-ossfuzz] [-pw-fuzztest] [-coverage] [-dmalloc] [-clang]linux-arm64-{rpc-console, all-clusters, all-clusters-minimal, chip-tool, thermostat, java-matter-controller, kotlin-matter-controller, minmdns, light, light-data-model-no-unique-id, lock, shell, ota-provider, ota-requestor, simulated-app1, simulated-app2, python-bindings, tv-app, tv-casting-app, bridge, fabric-admin, fabric-bridge, tests, chip-cert, address-resolve-tool, contact-sensor, dishwasher, microwave-oven, refrigerator, rvc, air-purifier, lit-icd, air-quality-sensor, network-manager, energy-management}Optional flags:
[-nodeps] [-nlfaultinject] [-platform-mdns] [-minmdns-verbose] [-libnl] [-same-event-loop] [-no-interactive] [-ipv6only] [-no-ble] [-no-wifi] [-no-thread] [-no-shell] [-mbedtls] [-boringssl] [-asan] [-tsan] [-ubsan] [-libfuzzer] [-ossfuzz] [-pw-fuzztest] [-coverage] [-dmalloc] [-clang] [-test] [-rpc] [-with-ui] [-evse-test-event] [-enable-dnssd-tests] [-disable-dnssd-tests] [-chip-casting-simplified] [-data-model-check] [-data-model-disabled] [-data-model-enabled] [-check-failure-die]linux-arm64-efr32-test-runnerOptional flags:
[-clang]
The
linux-arm64-chip-toolandlinux-arm64-all-clusterstargets were selected from the Linux section, with the-ipv6onlyand-platform-mdnsflags:./scripts/build/build_examples.py --target linux-arm64-chip-tool-ipv6only-platform-mdns gen cd ~/matter/connectedhomeip/out/linux-arm64-chip-tool-ipv6only-platform-mdns ninja -j 1 & disownBuilding the CHIP-Tool is a time-consuming process. To prevent SSH session timeouts, ninja was executed in the background. The job count was limited to 1 (
-j 1) to reduce memory usage.tail -f nohup.outcan be used to monitor the output.Move the built CHIP Tool:
mv ~/matter/connectedhomeip/out/linux-arm64-chip-tool-ipv6only-platform-mdns/chip-tool ~/matter/chip-tool rm -rf ~/matter/connectedhomeip/out/linux-arm64-chip-tool-ipv6only-platform-mdns
Step 5. Testing
Running CHIP Tool:
Commissioning
This section describes the Matter commissioning using CHIP Tool.
The following command should be run on the Commissionee to print the static configuration that includes the PIN code and Discriminator (0xf00 is 3840 in decimal):
Commissioning to Wi-Fi over BLE
A Commissionee joins an existing IP network over Bluetooth LE before being commissioned into a Matter network.
The following CHIP-Tool command starts commissioning onto a Wi-Fi network over BLE:
The parameters are defined as follows:
<NODE_ID_TO_ASSIGN>is the node ID assigned to the device being commissioned, which can be a decimal or hexadecimal number prefixed with ‘0x’.<SSID>is the Wi-Fi SSID, provided as a plain string or in hexadecimal format as ‘hex:XXXXXXXX’, where each byte of the SSID is represented as two-digit hexadecimal numbers.<PASSWORD>is the Wi-Fi password, given as a plain string or hex data.<PIN>is the PIN code for authentication.<DISCRIMINATOR>is the discriminator value.
CHIP-Tool starts the commissioning process, which includes the following steps:
Initialization
Initializes storage and loads key-value store (KVS) configurations.
Detects network interfaces and identifies the WiFi interface.
Sets up UDP transport manager and BLE transport layers.
Fabric and Node Setup
Loads the fabric table, which contains information about existing secure networks.
Creates a new fabric with a unique Fabric ID and Node ID.
BLE Scanning and Connection
Scans for nearby BLE devices.
Identifies the correct device using a discriminator match.
Establishes a BLE connection with the device.
Secure Session Establishment
Performs a PASE (Password Authenticated Session Establishment) handshake over BLE.
Exchanges secure messages to establish an encrypted session.
Marks the session as "Active" upon success.
Commissioning Process
Reads the device’s attributes and capabilities.
Arms a fail-safe mechanism to prevent accidental changes.
Configures the device based on regional regulatory requirements.
Certificate Exchange
The device provides PAI (Product Attestation Intermediate) and DAC (Device Attestation Certificate).
The system verifies the certificates and device authenticity.
Attestation and Verification
Validates the device’s attestation data to ensure a trusted identity.
Performs a revocation check to confirm the device’s legitimacy.
Operational Certificate Signing
The device generates a CSR (Certificate Signing Request).
The system issues a NOC (Node Operational Certificate) to authenticate the device in the network.
Finalizing the Pairing
Sends the root certificate to the device.
Marks the pairing process as "Success," making the device a trusted member of the Matter network.
Commissioning to Thread over BLE
The following CHIP-Tool command initiates commissioning onto a Thread network over BLE:
The parameters are defined as follows:
<NODE_ID_TO_ASSIGN>is the node ID assigned to the device being commissioned, which can be a decimal number or a hexadecimal number prefixed with ‘0x’.<OPERATIONAL_DATASET>is the Thread Operational Dataset, which contains the network credentials needed to join a Thread network. It is provided in hexadecimal format (hex:XXXXXXXX), where each byte of the dataset is represented as two-digit hexadecimal numbers.<PIN>is the PIN code for authentication.<DISCRIMINATOR>is the discriminator value.
Commissioning over Existing IP Network
A Commissionee already connected to a Wi-Fi, Ethernet, or Thread network can be commissioned without BLE discovery, using mDNS service discovery instead.
The following CHIP-Tool command commissions a device that is already connected to a Wi-Fi or Ethernet network:
The parameters are defined as follows:
<NODE_ID_TO_ASSIGN>is the node ID assigned to the device being commissioned.<PIN>is the PIN code for authentication.
The following CHIP-Tool command commissions a device that is already connected to a Thread network:
The parameters are defined as follows:
<NODE_ID_TO_ASSIGN>is the node ID assigned to the device being commissioned.<OPERATIONAL_DATASET>is the Thread Operational Dataset, which contains the network credentials for joining a Thread network.<PIN>is the PIN code for authentication.
Removing a Device from Fabric
The following CHIP-Tool command removes a device from the Matter Fabric:
The parameters are defined as follows:
<NODE_ID_TO_ASSIGN>is the node ID assigned to the device being removed.
Reading Device Attributes
The following command is used to read the current state of the "on/off" attribute from the target device:
In this command:
onoffis the cluster for controlling the power state.readis a request to retrieve the current state.on-offis the specific attribute being queried.0x1122is the hexadecimal node ID of the device.1is the endpoint number on the target device.
Similarly, the command below reads the measurement value from the temperature sensor:
Sending Commands to Device
The following command is used to turn on and toggle the device:
Subscribing to Attributes and Events
This section describes how to subscribe to attributes and events in a Matter device using CHIP-Tool.
Subscribing to Attributes
Display all the attributes available for subscription in a given cluster:
Subscribe to an attribute:
In this command:
cluster-name is the name of the cluster.
argument is the name of the chosen argument.
min-interval specifies the minimum number of seconds that must elapse since the last report for the server to send a new report.
max-interval specifies the number of seconds that must elapse since the last report for the server to send a new report.
node-id is the user-defined ID of the commissioned node.
endpoint_id is the ID of the endpoint where the chosen cluster is implemented.
For example:
Subscribing to Events
Display all the events available for subscription in a given cluster:
Subscribe to an event:
In this command:
cluster-name is the name of the cluster.
event-name is the name of the chosen event.
min-interval specifies the minimum number of seconds that must elapse since the last report for the server to send a new report.
max-interval specifies the number of seconds that must elapse since the last report for the server to send a new report.
node_id is the user-defined ID of the commissioned node.
endpoint_id is the ID of the endpoint where the chosen cluster is implemented.
For example: